Biology of Reproduction, lecture on Puberty
XV. Puberty
= Biological Transition, Child to Reproductive Adult
A. Pubescence = in the process of puberty
1. not development of 1o Sex Characteristics
a. Gonads
}all structures necessary
b. External Genitalia for mating
c. present at birth
2. not development of 2o Sex Accessory Structures
a. Vas deferens
b. Seminal Vessicles, Prostate Gland
c. uterus
d. also present at birth
3. Development of 2o Sex Characteristics
a. pubic hair, larynx growth,
breast development, facial hair
b. are not developed until puberty
i. both males and females
B. Maturation of Gonads, Germ Cells, &
internal reproductive organs
1. Menarche = time of first menstruation
a. maturation of oviducts, uterus, and vagina
b. not first ovulation necessarily
i. characteristically anovulatory cycles
ii. oligomenorrhea = menstrual cycles variable
in length
c. average age = 12.43 years
i. declining over the last 2 centuries
i. but not since 1973
2. First Ovulation or fertile ejaculation
a. Ovary: 500,000 follicles in a newborn
↑ 83,000 just before puberty
i. all lost to atresia since none are ovulated
C. Adolescence
1. time from puberty to Social adulthood
D. Maturation of Hormone Regulation
1. Controls the maturation process for maturation
of all other reproductive systems
a. 2nd critical window for neuroendocrine development
2. Rapid increase in production of gonadotropins
and sex steroids
3. Maturation of adrenal androgen production (adrenarche)
a. DHEA & DHEAS in males and females at 6 or 7
i. increased libido
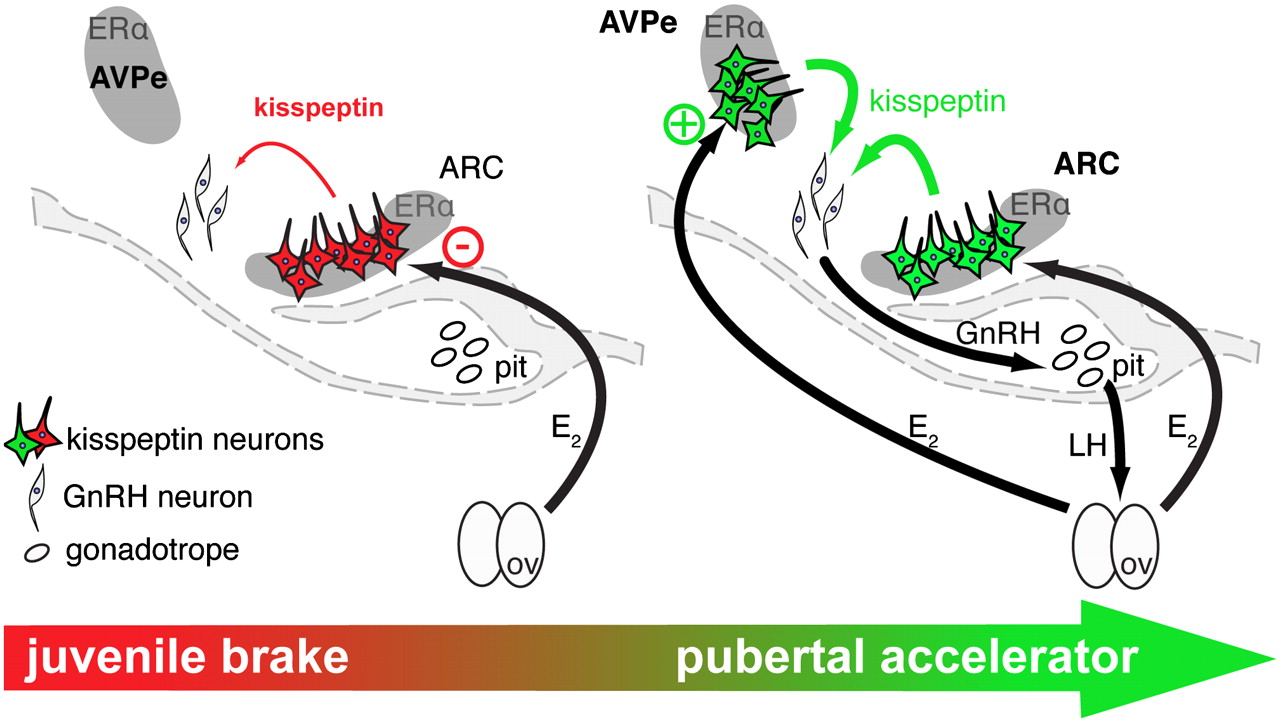
4. Maturation Kiss1 neurons and input to GnRH
a. Kiss1 development essential
i. intracranial Kp54 antagonist delays puberty
ii. ic Kp10 (Kp54 agonist) speeds up puberty
b. Fat → ↑ Leptin → ↑ Kiss1 + GPR54 mRNA
i. → ↑ Kiss1 in avPV and ARC
1) → ↑ on GnRH neurons
ii. TTF1 + CUX1-p200 transcription factors activate Kiss1 + GPR54 gene expression
c. E2 → ↑ Kiss1 mRNA → ↑ [Kp54]
i. females have more Kiss1 neurons
a. and earlier onset of puberty
1) neonatal synthetic E → ↑ Kiss1 mRNA
a) delays puberty
5. Feedback matures Endocrine responsiveness
a. Child has very low FSH & LH
and therefore low steroids
b. Low steroids in an adult would result high FSH and LH
because of low feedback
c. Set-point for feedback in the child is much lower
i. lower steroid levels shut off GnRH
1) set-point = gonadostat - may be controlled
by steroid receptor levels
2) set-point is 16x more sensitive in an child
than in an adult
ii. Set-point slowly changes at puberty
(1) gradual decrease "down regulation"
of steroid receptors?
(2) ~9 years to mature levels
male female
↑ sensitivity to ↓ sensitivity to
negative feedback negative feedback
Maturation of +feedback
(3) High levels of E2 in younger girls
does not result in an LH surge
d. maturation of GnRH pulse generator
in the medial basal hypothalamus
i. → ↑ amplitude and frequency of GnRH pulses
1) leptin from fat → ↑ ObRb → ↑ Kiss1 → ↑ Kp54 → ↑GPR54 → ↑GnRH
2) → ↑ NPY and Glu during puberty
a) NPY → ↑ Kiss1
b) NPY works with Gal
to stimulate GnRH release
(i) Gal colocalized with GnRH
in ARC neurons
e. GnRH receptors in the pituitary increase
during puberty
i. GnRH pulses maintain GnRH-R
f. LH and FSH receptors in the gonad increase
during puberty
i. maturation of LH & FSH pulsatility
ii. LH & FSH pulses ↑ during sleep
g. GnRH, LH and FSH pulsatility are necessary
for normal gonadal axis function in adults
E. Variation in the Timing of Puberty
1. 15% of variation in age of puberty
attributable to heredity
a. Identical Twins may be up to 2 months different
in the timing of menarche
b. Fraternal Twins - 8 months
2. Age of menarche has been declining
in developed countries
a. 3-4 months / decade
b. 1840 = 17 yrs 1900 = 14.2 1970's - 2002 = 12.3 yrs
i. now 12.43 yrs
3. Obese females tend to reach puberty earlier
a. females with very low body fat have delayed puberty
i. Primary Amenorrhea = delay of puberty
4. Critical Body Fat Hypothesis
a. % body fat is correlated with the age of puberty
b. evidence that critical body weight 45kg (104 lb)
must be obtained before puberty can begin
i. 17% of that must be fat
(1) enough fat to carry through a pregnancy
c. Fat cells have aromatase, convert androgen to E2
i. E2 from fat necessary to start first GnRH/LH surge
ii. Leptin from fat necessary to start first GnRH/LH surge
d. ↑fatcritical → ↑ Leptin → ↑ObRb → ↑ Kiss1 → ↑ Kp54 → ↑GPR54 → ↑GnRH, LH, FSH
i. anorexia → ↓ fat → loss of cyclicity:
leptin restores it
5. Stress →+ CRH →+ ACTH →+ F
a. CRH inhibits secretion of GnRH, and LH
b. ACTH also directly inhibits GnRH and LH,
but also FSH and E2 or T
c. Cortisol also directly inhibits
GnRH, LH, FSH E2 and T
i. inhibits cells from taking up fat,
amino acids, and sugar
ii. Ghrelin (gut hormone) → ↓ GnRH, LH
d. Adrenal Axis hormones (CRH, ACTH, F) also inhibit
reproductive behavior
e. Chronic Stress may delay puberty
i. stress at a very early age may
advance the age of puberty